M
0
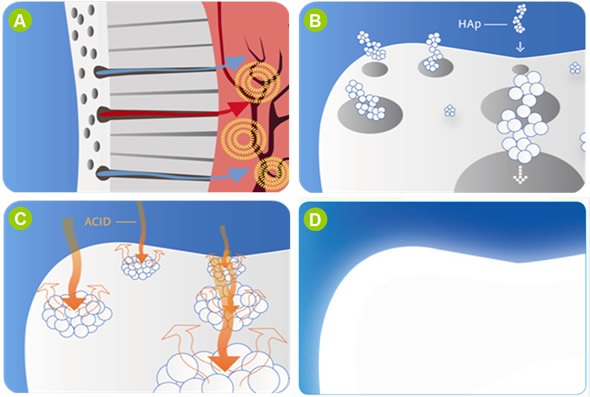
[h=2]Introduction[/thanks]Dental hypersensitivity is a major, common dental condition that occurs in approximately 57% of adults. Among individuals with periodontal disease, the prevalence can reach as much as 98% [1]. The condition usually arises as a result of continuous teeth erosion brought about by the action of foods, drinks and hot and cold temperatures that expose the dentin and underlying nerves, as shown in Figure 1A. As a result, external stimuli are transmitted to the nerves, causing brief but intense pain.
Dental hypersensitivity is usually treated by applying desensitizing toothpastes mainly composed by strontium chloride or ****ssium nitrate. However, these products do not simulate the natural composition and structure of dentin and enamel [2].
The mineralized tissues found in the human body are mostly composed of hydroxyapatite (HA), a natural calcium phosphate ceramic that is abundant in dentin (70%), enamel (97%) and bone (60%). Tooth enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body and is made up of building blocks of HA nanocrystals, 40nm in size. The tissue is acellular and unlike bone, cannot be naturally repaired [2]. Regenerating the surface of tooth enamel therefore poses a significant challenge.
[h=2]Nanohydroxyapatite Material[/thanks]In the past few years, considerable advances in the field of nanotechnology have led to a large number of nanomaterials being developed. In the healthcare sector, these novel materials are known to enhance the performance of diagnosis, treatments and disease prevention.
is one such material that is being utilized in medicine and dentistry, owing to its excellent bioactivity and biocompatibility as well as its similarity to the mineral component of teeth and bone. This calcium phosphate is already being used in oral care formulations and offers a number of benefits, such as effective reduction of teeth sensitivity [3, 4], fast enamel remineralization [5-7] and improved smoothness of tooth surface and whitening [8, 9].
Unlike microsized HA, the tiny nanoHA is easily integrated into the dental tubules, enhancing their occlusion (Figure 1B). This seals the tubules and prevents exposure of the nerves to external stimuli, thereby reducing dental hypersensitivity. Moreover, nanoHA has a higher surface area, biological activity and chemical reactivity, which facilitate its binding to the dentin apatite and tooth enamel. This creates a new apatite layer that remineralizes the enamel and protects the surface of the tooth. This layer protects the tooth from the damage caused by acids in food and drink (Figure 1C) as well as whitening the tooth and making it smoother, as shown in Figure 1D [2].
[h=2]nanoXIM
Dental hypersensitivity is usually treated by applying desensitizing toothpastes mainly composed by strontium chloride or ****ssium nitrate. However, these products do not simulate the natural composition and structure of dentin and enamel [2].
The mineralized tissues found in the human body are mostly composed of hydroxyapatite (HA), a natural calcium phosphate ceramic that is abundant in dentin (70%), enamel (97%) and bone (60%). Tooth enamel is the hardest tissue in the human body and is made up of building blocks of HA nanocrystals, 40nm in size. The tissue is acellular and unlike bone, cannot be naturally repaired [2]. Regenerating the surface of tooth enamel therefore poses a significant challenge.
[h=2]Nanohydroxyapatite Material[/thanks]In the past few years, considerable advances in the field of nanotechnology have led to a large number of nanomaterials being developed. In the healthcare sector, these novel materials are known to enhance the performance of diagnosis, treatments and disease prevention.
is one such material that is being utilized in medicine and dentistry, owing to its excellent bioactivity and biocompatibility as well as its similarity to the mineral component of teeth and bone. This calcium phosphate is already being used in oral care formulations and offers a number of benefits, such as effective reduction of teeth sensitivity [3, 4], fast enamel remineralization [5-7] and improved smoothness of tooth surface and whitening [8, 9].
Unlike microsized HA, the tiny nanoHA is easily integrated into the dental tubules, enhancing their occlusion (Figure 1B). This seals the tubules and prevents exposure of the nerves to external stimuli, thereby reducing dental hypersensitivity. Moreover, nanoHA has a higher surface area, biological activity and chemical reactivity, which facilitate its binding to the dentin apatite and tooth enamel. This creates a new apatite layer that remineralizes the enamel and protects the surface of the tooth. This layer protects the tooth from the damage caused by acids in food and drink (Figure 1C) as well as whitening the tooth and making it smoother, as shown in Figure 1D [2].

Figure 1. (A) Exposure of dentin tubules to hot and cold temperatures stimulates nerves and causes pain; (B) nanoHA fills dentin tubules binding chemically to dental structure reducing hypersensitivity; (C) nanoHA remineralizes the tooth enamel protecting it against acid attacks from food and beverages; (D) improved smoothness and whitening due to enamel repair by nanoHA.[h=2]nanoXIM
