M
0
Introduction To Maya Fluids
Published 11/2022
MP4 | Video: h264, 1280x720 | Audio: AAC, 44.1 KHz
Language: English | Size: 748.61 MB | Duration: 0h 44m
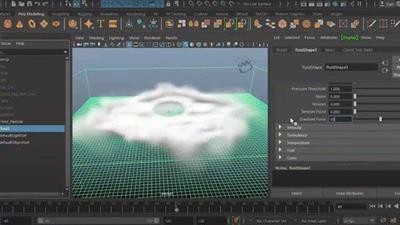
Creating Cloud Using Autodesk Maya Fluids
Published 11/2022
MP4 | Video: h264, 1280x720 | Audio: AAC, 44.1 KHz
Language: English | Size: 748.61 MB | Duration: 0h 44m
Creating Cloud Using Autodesk Maya Fluids
What you'll learn
Introduction to Maya fluids with nparticle Goal and Expression
Creating Cloud with helps of Maya Fluids
How to work together with Maya fluids and nparticle
Maya nparticle and Expression
Requirements
Basic Knowledge of Autodesk Maya
Description
A. For Over All Quality 1. Base Resolution 2. Hi Details Solver 3. Substeps /////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// B. Fluid Dynamic Simulation attributes 1.Gravity The Gravity setting is a built-in gravitational constant that simulates the gravitational attraction of the mass of the world in which the simulation is occurring. Negative values cause a downward pull (relative to the world coordinate system). If Gravity is zero, Density Buoyancy and Temperature Buoyancy have no effect 2.Viscosity Viscosity represents the resistance of the fluid to flow, or how thick, and non-liquid the material is. When this value is high, the fluid flows like tar. When this value is small, the fluid flows more like water. 3.Friction Defines internal friction used in Velocity solving. 4.Damp Defines the amount the Velocity solution. Small amounts of damping can be useful when boundaries are open to keep strong winds from building up and leading to instability. ///////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// C. Content Details Density Important Section 1. Density Scale Over All Scale 2. Buoyancy Help to expend Fast Positive And Negative Side 3. Dissipation Disappear of Fluids 4. Diffusion Crate Blurriness effect inside Container 5. Density Pressure Outward Furse For Expend Fluids(explosion, Blast, Dense Smoke) 6. Density Tension For Help to create Spherical shape, Rounded Shapes 7. Tension Force It will help to smooth and Improve Density Tension 8. Gradient Force All About Air //////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////////// D. Temperature 1.Temperature Scale Multiplies the Temperature values defined in the container. 2.Buoyancy Defines built-in buoyancy strength for Temperature solving. 3.Pressure Pressure simulates the increase in pressure that results from the increasing temperature of a gas, which causes the fluid to expand quickly. To see the full effects of Pressure in the fluid, turn on Forward Advection. Pressure is useful for explosion effects as it can cause a small amount of emitted fluid to quickly expand with turbulent motion. 4.Dissipation Defines the rate at which the Temperature gradually dissipates in a grid. At each time step, Temperature is removed from each voxel (the Temperature value becomes smaller). 5.Pressure Threshold Specifies the temperature value at which Pressure is applied on a per voxel-basis. For voxels that have temperature lower than Pressure Threshold, no Pressure in applied. 6.Diffusion Defines the rate at which the Temperature diffuses between voxels in a Dynamic Grid. 7.Turbulence Multiplier on the turbulence applied to the Temperature. 8.Noise Randomizes the temperature values of voxels each simulated step. Noise is applied to temperature in constant amounts that are not affected by changes in velocity. You can use Noise to add detail to smooth flowing effects and to the texture grids. Noise can creates effects similar to Turbulence, but differs in the way it creates randomization. Noise randomizes temperature values each step, while Turbulence randomizes the velocity based on the Temperature grid. 9.Tension Tension pushes temperature into rounded shapes, making the temperature boundaries more defined in the fluid. When set to high values, Tension can force fluid temperature into individual areas of in the grid. The effect of Tension in a fluid effect is similar to the effect of surface tension in liquids. Tension does not affect velocity in voxels. You can use Tension to add puffiness to cloud and smoke effects. Tension can also be used to remove artifacts that appear when using High Detail Solve.
Overview
Section 1: MAYA FX
Lecture 1 Emit fluids on nparticle
Lecture 2 Fluids_Emitter_Settings
Lecture 3 Fluids Container Settings
Lecture 4 Apply Volume Curve External Force
Lecture 5 Final Output
Section 2: Create Thick Smoke
Lecture 6 Create Thick Burn Effect
Beginners
Download link
rapidgator.net:
You must reply in thread to view hidden text.
uploadgig.com:
You must reply in thread to view hidden text.
nitroflare.com:
You must reply in thread to view hidden text.
1dl.net:
You must reply in thread to view hidden text.

